Also Read
Introduction
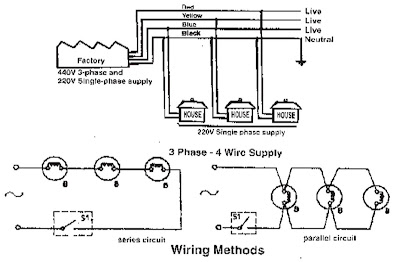
Power is supplied to the domestic installations through, the phase and a neutral, forming a single phase A.C. 230V, two wire system. For industrial establishments, power is supplied through three-phase four-wire system to give 440V. Figure shows the power tapping for domestic and industrial purposes. The neutral is earthed at the sub-station of the supply. As a safe practice all single-phase devices such as switches, fuses etc., are connected to the live conductor. All electrical conductors and cables are colored coded and must be correctly connected up. Electrical wiring is defined as a system of electrical conductors, components and apparatus for conveying electrical power from the source to the point of use. The wiring system must be designed to provide a constant voltage to the load.Elements of House wiring:
1. Fuses and circuit breakers2. Electrical switch
3. Plug
4. Socket outlet
5. Lamp holder
6. Ceiling Rose
7. Main switch
8. Incandescent light
Wires and wire sizes:
A wire is defined as a bare or insulated conductor consisting of one or several strands. An insulated wire consists of a conductor (Silver/Copper/Aluminium) with insulating material made of vulcanized Indian Rubber (VIR) or Poly Vinyl Chloride (PVC). Wire sizes are specified by the diameter of the wire, using a standard wire gauge (SWG), which also gives an idea of the current carrying capacity. The specification consists of both the number of strands and diameter of each wire in it. For Example, the specification 3/18 PVC consists of 3 strands of 18 gauge each.Various systems of wiring:
- Cleat wiring
- C.T.S. / T.R.S.Wiring (Cap tyer sheathed/ Tough rubber sheathed wiring)
- Wooden casing & capping wiring
- Lead sheathed wiring
- Conduit wiring
- PVC casing & capping
Wiring methods:
2. Parallel circuit
Fundamentals of Electricity:
Electrical symbols :Voltage: It is a pressure which makes the electricity to flow. The unit of measure is Volt. The symbol used is ‘V’. The instrument used to measure is Voltmeter.
Current: The free flow of electrons is called as current. The unit to measure current is ‘Ampere’. The symbol is ‘A’. The instrument used to measure the current is Ammeter. Resistance: It is opposition to current. The unit of resistance is ‘Ohm’. The symbol of ohm is Ω. The resistance is measured by Ohmmeter.
Watt: It is the rate of doing work, when potential difference across the current is of volt and current flowing is ampere per second.
The energy consumed is of Watt.
1000 Watts = 1 Unit
746 Watts = 1 H.P.
The following are the formulae for calculation.
Voltage V or E = W / I = ÖWR = IR
Current I = E / R = W / E = ÖW / R
Resistance R = E2 / W = E / I = W / I2
Wattage W = I2R = EI = E2 / R
House Wiring Tools:

Combination Pliers : Used for holding, twisting or cutting of wires.
Side cutting Plier: Used for Cutting at narrow places or ordinary places for removing insulation.
Round Nose Plier or Flat Nose Plier: Used for holding, twisting or joining the wire at narrow places.
Firmer Chisel: Used for chipping, scrapping and grooving the wood.
Cold chisel: Used for chipping, Boring and channeling in walls. Tenon saw or back Saw: Used for cutting wooden boards, Block casting etc.
Hack saw: Used for cutting conduit GI pipes or mild steel.
Mallet: Used as a hammer and made of wood Double Blade Electric knife: It has two blades, one for removing insulation of wires and another for cleaning the wires
Soldering Iron: Used to solder small joint terminals Poker: Used for making pilot holes for fixing wood screws.
Line Tester: Used for testing the current.
Royal Plug Tool: It is made of steel and is used for making holes in the stone wall or concrete wall for fibre made Royal plugs.
Screw driver: Used for loosening, tightening and to keep the screws in position.
Ball Peen Hammer: Used for fitting nails in the walls or wooden boards.
Instructions:
- When closing the electric switch, always grasp the switch by the insulated handle.
- Do not run too many electrical items from one point.
- Use fuses and circuit breakers of proper capacity, so as to interrupt the current before it becomes dangerous.
- Disconnect the units to be repaired free from power supply and make sure that they might not be energized while the repair work continues.
- Do not pour water to put-off fires in electric wires and electric equipment. You will be subjected to electric shock or you will be electrocuted. Use sand to put-off fires in electric items.
- Whenever there is power failure, put-off the power supply to all equipment, in order to prevent spontaneous recovery.
- Never remove a plug from an outlet by pulling cord. Always pull by holding the plug.
- While testing always keep one hand in your packet. If the hands are in contact with a circuit, current will flow across your body and is more dangerous.
- Electricity has no respect for ignorance. Do not apply voltage or turn-on any device until it has been properly checked.
- Check earth connection before switching on portable equipment
.
Safety Precautions :
1. First we should be insulated2. Care should be taken while fixing the fuse
3. All the switches should be off before power supply.
4. When power is on, the terminal wires should not be touched










Comments