Also Read
UPSETTING
- Increases the thickness (or diameter) of a bar and reduces its length.
- Portion of the bar which is to be upset is heated locally.
- Blow of the hammer must be in line with the bar to prevent bending of the bar.
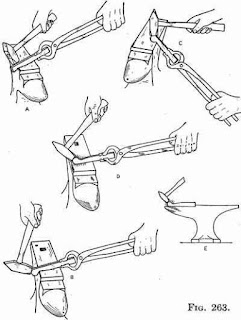
BENDING
- Bending of bars, flats and other similar stock material is usually done in a smithy shop. This can be done to produce different types of bent shapes such as angles, ovals and circles, etc.
- Any desired angle can be made through this operation. For making a right angle bend that particular portion of the stock, which is to be subjected to bending, is heated and jumped on the outer surface.
- This operation is carried out on the edge of the anvil or on the perfectly square edge of a rectangular block. After bending, the outside bulging is finished by means of a flatter and the inside one by means of a set hammer.
- Curved shapes of bends are formed on the horn of the anvil. For mass production of articles made through bending, particularly when dimensional accuracy is a must, jigs and fixtures are designed to help in performing this operation quickly and efficiently. This results in a considerable saving of time and labour.
DRAWING DOWN
- This process is also known as drawing out. It is exactly a reverse process to that of upsetting in the sense, it is employed when a reduction in thickness, width or both of a bar is desired with a corresponding increase in its length. The desired effect is possible to be obtained by the use of either the peen of a cross peen hammer, a set of fullers or a pair of swages (for round bars only).
- The process of heating and cooling the length, not required to be drawn, is the same as in case of upsetting, but the selection of the above tools is governed by the shape of the cross-section of the stock, the amount by which the increase in length is desired and also the required finished shape of the job.
PUNCHING and DRIFTING
- Punching and drifting are used for producing and finishing holes and preparatory for producing other shapes.Punching should be done in two stages.
- In the first stage the work piece is kept flat on the anvil and holes performed half way through. Then job is turned upside down.
- The application of punching, producing the slot a number of holes are punched and the remaining excess material is cut out using a chisel. The slot may then be finished hot drifting or may be finished by filing when cold.
- Drifting: By this process punched hole enlarged.
 |
| Drifting |
FLATTENING
- Reduce the thickness of job to required shape.
- The flattening is carried out after drawing out, fullering or any other operation to remove the fullering marks for leveling and finishing flat surfaces
FULLERING
- Heated stock is placed on Fuller fixed on Anvil.
- A Fuller is put over the stock and hammering is done.
- Reduce the cross section of the job at required point.
SWAGING
- Produce a bar with a smaller diameter (using concave dies).
- Usually done at the ends to make metal ready for next forming process.
- Provides a reduced round cross section suitable for taping, threading, upsetting.






















Comments