Also Read
%save the function with name as plotcube.m
%function starts from here
function plotcube(varargin)
% PLOTCUBE - Display a 3D-cube in the current axes
%
% PLOTCUBE(EDGES,ORIGIN,ALPHA,COLOR) displays a 3D-cube in the current axes
% with the following properties:
% * EDGES : 3-elements vector that defines the length of cube edges
% * ORIGIN: 3-elements vector that defines the start point of the cube
% * ALPHA : scalar that defines the transparency of the cube faces (from 0
% to 1)
% * COLOR : 3-elements vector that defines the faces color of the cube
%
% Example:
% >> plotcube([5 5 5],[ 2 2 2],.8,[1 0 0]);
% >> plotcube([5 5 5],[10 10 10],.8,[0 1 0]);
% >> plotcube([5 5 5],[20 20 20],.8,[0 0 1]);
% Default input arguments
inArgs = { ...
[5 5 5] , ... % Default edge sizes (x,y and z)
[10 10 10] , ... % Default coordinates of the origin point of the cube
1 , ... % Default alpha value for the cube's faces
[1 0 0] ... % Default Color for the cube
};
% Replace default input arguments by input values
inArgs(1:nargin) = varargin;
% Create all variables
[edges,origin,alpha,clr] = deal(inArgs{:});
XYZ = { ...
[0 0 0 0] [0 0 1 1] [0 1 1 0] ; ...
[1 1 1 1] [0 0 1 1] [0 1 1 0] ; ...
[0 1 1 0] [0 0 0 0] [0 0 1 1] ; ...
[0 1 1 0] [1 1 1 1] [0 0 1 1] ; ...
[0 1 1 0] [0 0 1 1] [0 0 0 0] ; ...
[0 1 1 0] [0 0 1 1] [1 1 1 1] ...
};
XYZ = mat2cell(...
cellfun( @(x,y,z) x*y+z , ...
XYZ , ...
repmat(mat2cell(edges,1,[1 1 1]),6,1) , ...
repmat(mat2cell(origin,1,[1 1 1]),6,1) , ...
'UniformOutput',false), ...
6,[1 1 1]);
cellfun(@patch,XYZ{1},XYZ{2},XYZ{3},...
repmat({clr},6,1),...
repmat({'FaceAlpha'},6,1),...
repmat({alpha},6,1)...
);
view(3);
%save this program with another name
axis([0 25 0 25 0 25]);
grid();
%function ends
%create new m-File and save cum run the program
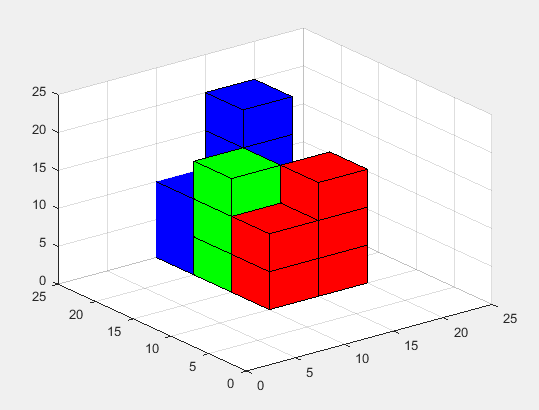
plotcube([10 10 10],[10 20 0],1,[0 0 1]);
plotcube([5 5 5],[15 20 0],1,[0 0 1]);
plotcube([5 5 5],[15 20 5],1,[0 0 1]);
plotcube([5 5 5],[15 20 10],1,[0 0 1]);
plotcube([5 5 5],[15 20 15],1,[0 0 1]);
%creating greeen color cubes
plotcube([5 5 5],[10 15 0],1,[0 1 0]);
plotcube([5 5 5],[10 15 5],1,[0 1 0]);
plotcube([5 5 5],[10 15 10],1,[0 1 0]);
plotcube([5 5 5],[15 15 0],1,[0 1 0]);
%creating red color cubes
plotcube([5 5 5],[10 10 0],1,[1 0 0]);
plotcube([5 5 5],[10 10 5],1,[1 0 0]);
plotcube([5 5 5],[15 10 0],1,[1 0 0]);
plotcube([5 5 5],[15 10 5],1,[1 0 0]);
plotcube([5 5 5],[15 10 10],1,[1 0 0]);







Comments